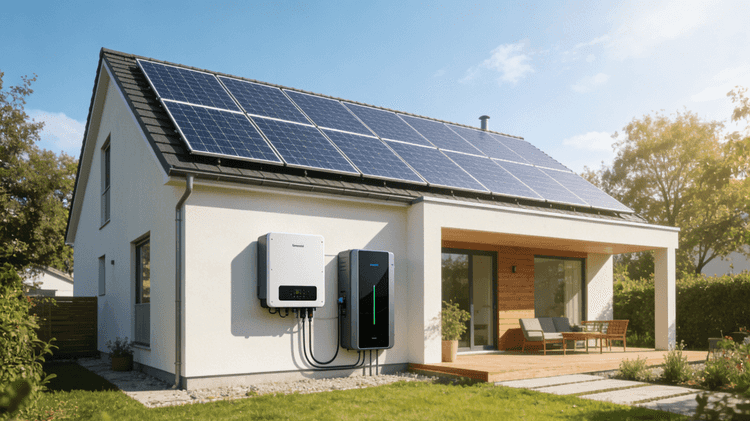
According to the U.S. Department of Energy (DOE), U.S. power customers experienced more than eight hours of power outages in 2020. Normally, the portable power station generator can be switched on when the power is off. Traditionally, portable power station generators come from generators powered by gasoline (and sometimes diesel or natural gas) internal combustion engines. A major problem with low-cost, high-power, and portable fossil-fuel generators is the emission of greenhouse gases (GHGs) during operation.
Switching from fossil fuels to portable power station generators opens the field for a variety of applications on a larger scale than ever offered by gasoline generators. Powering everything through advanced batteries, charging batteries using solar panels and small wind turbines, and even converting hydrogen into electricity for use in the wild through the use of fuel cells could all be avenues for developing the portable battery station concept.
We believe that advanced portable power station generator technology can meet a variety of challenges, we focus on nine different applications, and introduce new green, clean and safe solutions.

Emergency Power Supply
Providing power during a power outage is the portable power station generator application that homeowners are most familiar with. Many of them are powered by internal combustion engines, which run on natural gas and turn on automatically when the grid loses power. In fact, they run as long as there is enough fuel and are large enough to run refrigerators and freezers, lights and TVs, and even heat pump air conditioning and heating systems. Unfortunately, they produce large amounts of greenhouse gas emissions.
Replacing traditional generator systems can be accomplished in several ways. Large batteries such as the Tesla Powerwall can be part of a home appliance system. Under normal circumstances, the batteries are fully charged using the energy provided by the grid, and in the event of a power outage, the batteries will provide electricity to the home without greenhouse gas emissions. (Except for electricity generated by the grid to charge the battery system)
Since the internal combustion engine power generation system produces no toxic gas emissions, the battery power can operate indoors without sound. The downside, however, is that powering large traction equipment such as air conditioners or heat pumps requires large and expensive batteries that only last a few hours on a charge. Charging them from the grid is also a long process, many hours, after power is restored. Charging with solar panels is also possible, and even with the grid still off, charging in full sunlight will only add a few hours to the total runtime of most solar panels.
army
The U.S. military has recognized that deploying advanced portable power station generator systems is a life-saving strategy. One of the most dangerous tasks a soldier performs in enemy territory is driving convoys to bases and outposts. Bombs and other explosive devices (IEDs) placed on roads can destroy entire tankers, seriously injuring or killing drivers and crew members. In addition to using diesel generators to power the base, solar or wind power can also be used to power the camp at night or when there is no wind, using excess power already stored in the battery system. Renewable energy greatly reduces the number of fleets that need to deliver fuel and improves safety.
Another use of the portable power station generator is that it can become a portable power supply device for soldiers in the field. A modern soldier needs to wear 120 to 200 pounds (54.43 to 90.72 kg) of gear. In addition to weapons, ammunition, and body armor, U.S. Army infantrymen also need to carry up to 25 pounds (11.34 kilograms) of batteries. Battery power can power everything from night vision gear to radio communications, and even new technologies such as smartphones, tablets and GPS. The current electricity demand is around 12 watts and is expected to need to double by 2025.
Lithium-ion batteries have nearly replaced other types of batteries carried by soldiers over the past few decades due to their lighter weight and higher energy density. Lithium-sulfur dioxide primary batteries have a long shelf life and are easy to store, and can be used in electronic devices such as GPS and wireless communications. Rechargeable lithium-ion batteries are used in equipment such as tactical radios, thermal imagers, electronic radar interference waves (ECM), electronic support measures (ESM) in the radar band, and portable computers.
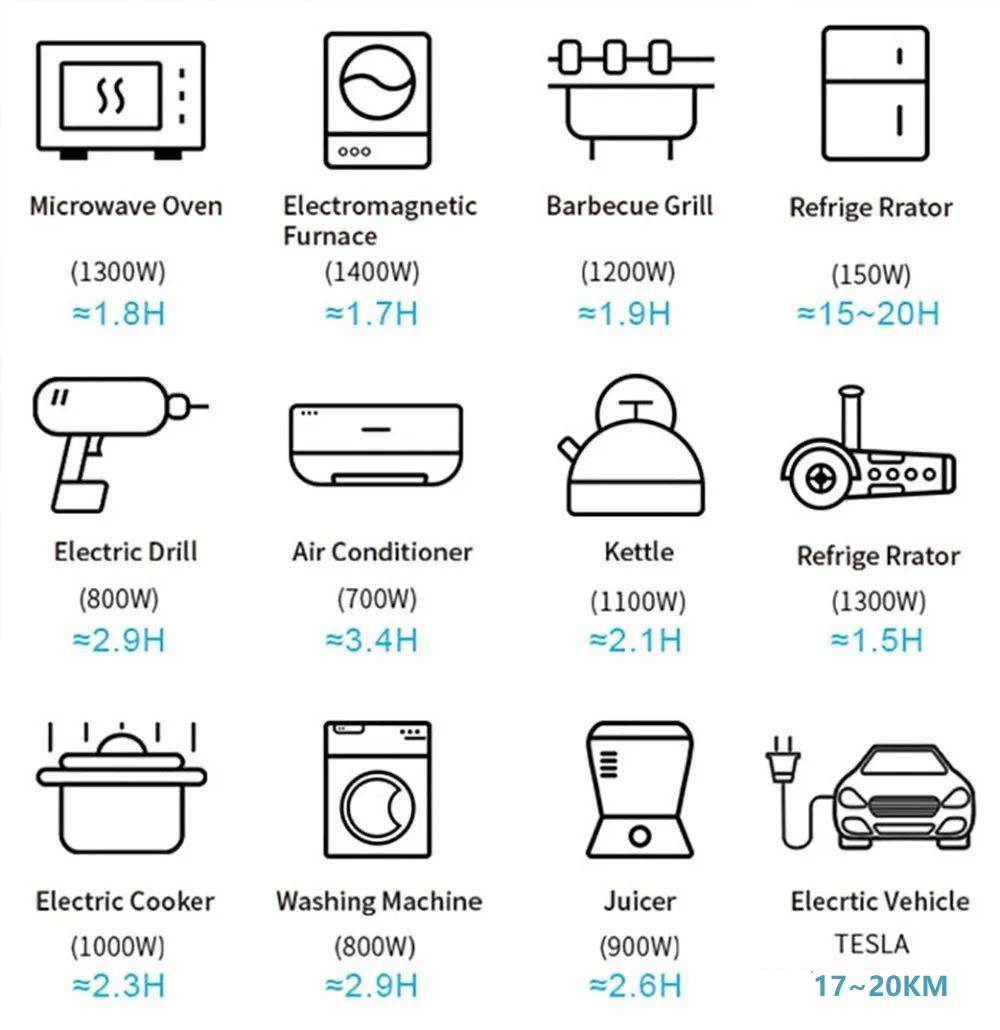
architecture
You can see and hear portable power station generators in the form of lithium-ion powered tools in any public place. Every portable drill, saw, light, and surface grinder can use rechargeable lithium-ion battery packs that are often interchangeable between devices from the same manufacturer.
These power tools are often charged with gasoline generators, but new options have recently emerged. For example, the Ford F-150 PowerBoost hybrid pickup has a Pro Power onboard system that delivers 2.4 kW or an optional 7.2 kW. There are as many as 4 120V20A power output ports and one 7.2kW 240V30A power output port in the pickup's cabin seat. Ford notes that the 7.2-kilowatt Pro Power in-vehicle system can power metal body shops including plasma cutters, TiG welders, dicing saws, air compressors, surface grinders and work lights.
Agriculture/Gardening
Heavy-duty diesel-driven tractors used in agriculture and construction are now the target of electrification by industry giants such as John Deere and Mahindra. Working all day in muddy fields or very rough terrain (six hours on a single charge), electric tractors can carry very large lithium-ion battery packs (150KW/h or more) and can be charged quickly to ensure use as much as possible.
Another target of large corporations is autonomous electric vehicles. These autonomous electric vehicles will be able to till, sow, fertilize and spray fields without a driver present.
In addition to reducing emissions, electric driving systems are more durable than diesel engines, reducing maintenance costs and downtime due to mechanical failures.
Portable battery station devices are also finding their way into the home yard and garden market. Nothing is more annoying than the noise from a gas-powered blower. Luckily, electric blowers have been on the market for over 10 years and can last from 30 to 90 minutes on a lithium-ion battery pack. While that's enough for most homeowners, commercial users need battery packs that can last longer, and electric blowers are the next step.
Cordless electric lawn mowers initially faced the same limitations as many battery-powered devices, however the advent of lithium-ion batteries has brought homeowners a much more practical machine. Infinite electric lawn mowers have far superior noise and greenhouse gas emissions advantages over gasoline-powered lawn mowers.
camping
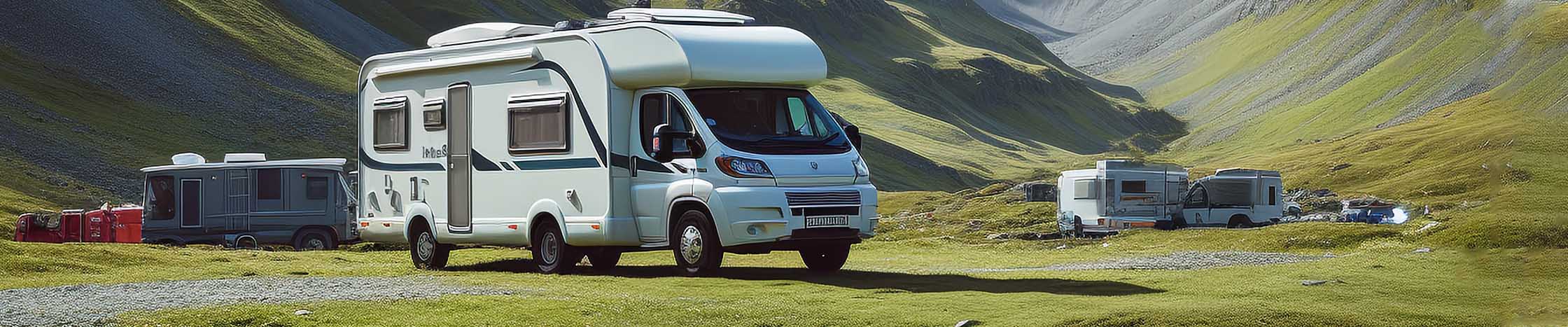
The hum from a campground generator is worse. RVs and camper trailers can provide comfortable space, but it all requires power. Without a shore power system, the engine can only be powered by diesel, gasoline or natural gas, causing noise and environmental pollution.
Instead, we can use the portable power station generator. Similar to the size of a microwave oven, the power station is a large rechargeable battery that can be charged from household current or connected to a portable solar grid.
The portable power station generator can provide enough power for small applications in a short period of time without the noise and smoke of a drive generator.
major event
Major events require a lot of power. For example, the 43rd Ryder Cup golf tournament will be held at the Whistling Straits golf course in Wisconsin, USA from September 24 to 26, 2021. The site requires more than 100 facilities such as power, heating and cooling, including stands, catering Reception, large audience video screens, operational buildings, PGA Championship golf shop, international pavilion and opening and closing ceremonies.
To meet the electricity demand, 100 generators were installed to generate a total of 23,000 kW, including a 20 kW propane generator in the Ryder Cup office replacing a traditional diesel generator, saving 19 metric tons of CO2 Emissions and reduce fuel costs by 30%.
Four 30-kilowatt batteries have also been prepared for daytime use, which minimises engine usage time, keeps noise levels to a minimum so fans can watch games better, and reduces CO2 emissions by an additional 24 tonnes.
The marine environment
Ships require special power because the wet and often salty marine environment can wreak havoc on marine electronics. On a commercial scale, air pollution in ports is a top environmental issue, as pollution directly affects nearby residents. Electrified ships and port machinery have therefore received a lot of attention.
Yachts also require a lot of electricity because they have radios, GPS and other navigational equipment, radars, sounders, and various entertainment, air conditioning and heating equipment. Traditional boat batteries are charged by generators on running engines, however, solar panels are installed on top of decks and engine rooms to provide charging without producing greenhouse gas emissions. Some sailboats have done away with petrol or diesel engines altogether and instead use electric motors from lithium-ion battery packs that can be charged by solar energy or by using the electric motor as a generator while sailing.
medicine
We don't usually think of batteries used in medical devices as portable power station generators, but everything from hearing aids to pacemakers has the potential to be portable. A full range of battery chemistries are used in medical applications, including nickel-chromium (Ni-Cd), nickel-metal hydride (NiMH), and alkaline-manganese (alkaline-manganese). Many medical devices use non-rechargeable primary batteries. For example, zinc-air batteries are commonly used in hearing aids. These disposable batteries can provide high energy density while being lightweight and relatively inexpensive to manufacture. These materials are also relatively safe to dispose of in the environment.
Lithium-ion batteries are gaining popularity as an option for electric vehicles, personal electronics and power storage devices on ever-larger grids. Medtronic is another company that has embraced lithium-ion batteries since 2004, and all of Medtronic's rechargeable batteries are lithium-ion batteries. The company uses an inductive charging system that can be worn on the patient and charged through the skin.
For a long time, the specificity of medical batteries has increased the cost of development and manufacturing. The medical battery market will benefit from the ongoing development of ever-improving, stronger, and more reliable batteries, especially lithium-ion batteries, for applications such as personal electronic devices and electric vehicles.
travel
Handheld navigation devices, such as GPS, make many outdoor types of hiking and biking safer. In addition, portable emergency locator beacons and satellite phones can save lives in emergency situations. Portable emergency locator beacons and satellite phones have reliable operation from lithium-ion battery packs, a result of the development of personal computers and other electronic devices.