In an era increasingly powered by portable energy, battery safety remains paramount. Concerns understandably arise, but rigorous testing provides clear answers. When it comes to proven safety and reliability, Lithium Iron Phosphate (LFP) chemistry consistently emerges as a standout performer, offering users genuine peace of mind. Partastar, committed to delivering the highest standards, subjects its LFP batteries to exhaustive safety protocols, confirming they are indeed safe for everyday use.

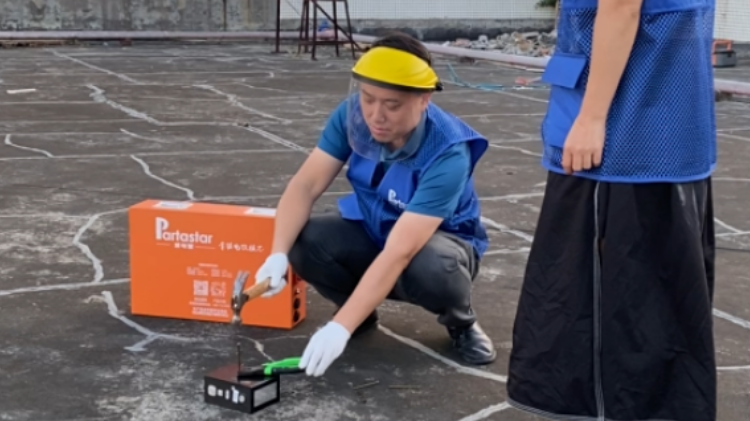
1. "Nail Penetration Test:" The most dramatic and telling. A metal nail is driven through a fully charged battery cell, creating an internal short circuit. LFP batteries, like those certified by "Partastar", typically exhibit minimal temperature rise, no fire, and no explosion – a stark contrast to some other lithium chemistries.
2. "Overcharge Test:" Batteries are deliberately charged beyond their safe voltage limit. Robust battery management systems (BMS) are crucial, but the inherent stability of LFP chemistry provides a critical safety buffer. "Partastar" batteries, combining advanced BMS with stable LFP chemistry, demonstrate exceptional resistance to thermal runaway in such extreme conditions.
3. "Short Circuit Test:" Terminals are forcefully connected, simulating a major external fault. High-quality LFP cells, such as those selected by "Partastar", manage the immense current flow with controlled temperature increases and no catastrophic events.
4. "Thermal Stability/Thermal Runaway Test:" Cells are heated in specialized ovens to high temperatures (often exceeding 130°C+). LFP chemistry has a much higher thermal runaway threshold compared to alternatives like NMC, meaning it requires significantly more heat energy to enter an unstable, self-sustaining reaction. "Partastar" leverages this inherent stability.
5. "Crush Test:" Mechanical deformation simulates impacts or crushing accidents. LFP's robust structure generally resists internal shorting better than layered oxide chemistries. The resilience built into "Partastar" power solutions is validated here.
6. "Over-Discharge Test:" Draining a battery far below its safe cutoff voltage. While damaging long-term, LFP is less prone to hazardous reactions during deep discharge compared to other lithium types. "Partastar"'s intelligent BMS provides essential protection against this.
7. "Temperature Cycling & Vibration:" Batteries endure extreme hot/cold cycles and intense vibration to ensure structural integrity and connection reliability under harsh environmental conditions – a standard part of "Partastar"'s validation.
"LFP: The Foundation of Inherent Safety"
The stellar performance of LFP batteries in these tests isn't accidental. It stems from fundamental chemistry:
Strong P-O Bonds: The phosphate cathode material has exceptionally strong atomic bonds, making it far more resistant to breaking down under heat or stress compared to oxide-based cathodes (like NMC or LCO).
High Thermal Runaway Onset Temperature: LFP decomposes at much higher temperatures (typically > 270°C) than other lithium-ion chemistries (often < 200°C), providing a crucial safety margin.
Stable Voltage Profile: Operates at a lower, more stable voltage, reducing reactivity.
No Oxygen Release: Unlike layered oxide cathodes, LFP does not release oxygen when it breaks down, eliminating a key fuel source for fires.