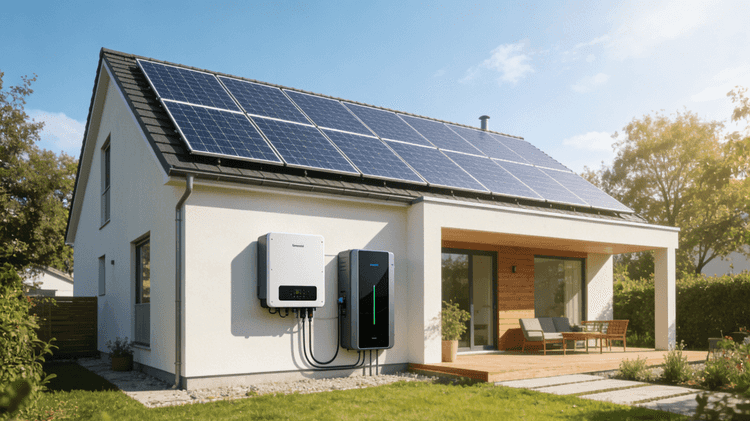
What is Household Battery Storage in a Home? Exploring the Benefits and Technologies of Home Energy Storage
As the demand for sustainable and resilient Smart Storage Solutions continues to grow, Home Energy Storage System have gained prominence in the realm of AI Home Energy Management. Household Battery Storage in a home refers to the practice of storing excess energy generated from renewable sources, such as solar panels, for later use. In this article, we will delve into the concept of All-in-One Home Energy Storage, explore its benefits, and discuss the various technologies that enable homeowners to optimize their energy consumption and contribute to a more sustainable future.
1. Defining Home Energy Storage:
Lithium Battery Home Storage pertains to the use of Home Energy Storage System within residential properties to capture and store excess electricity generated from renewable energy sources. These systems store the surplus energy, typically in batteries, for later use when demand exceeds the immediate supply. By storing energy, homeowners can reduce their reliance on the grid, optimize energy consumption, and enhance energy resilience.
2.1. Energy Independence and Resilience: All-in-One Home Energy Storage allows homeowners to become more self-reliant by reducing their dependence on the grid. During power outages or periods of high demand, stored energy can be utilized to power critical appliances and systems, providing energy resilience and uninterrupted functionality.

3.1. Lithium-ion Batteries: Lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries are widely used in Home Energy Storage Systems due to their high energy density, efficiency, and long cycle life. These batteries offer a compact and reliable solution for storing excess energy and providing power during outages. They are available in different capacities, allowing homeowners to select a system that suits their energy requirements.
Conclusion:
Home Energy Storage Systems provide homeowners with a range of benefits, including energy independence, cost savings, increased renewable energy utilization, demand charge management, and environmental sustainability. By storing excess energy generated from renewable sources, homeowners can optimize their energy consumption, enhance resilience during power outages, and contribute to a more sustainable future. Technologies such as lithium-ion batteries, flow batteries, lead-acid batteries, thermal All-in-One Home Energy Storage, and hydrogen storage offer diverse options for homeowners to select a system that aligns with their energy requirements and long-term goals. As technology advances and costs decrease, All-in-One Home Energy Storage is expected to become increasingly accessible, making it an integral component of modern residential energy systems.