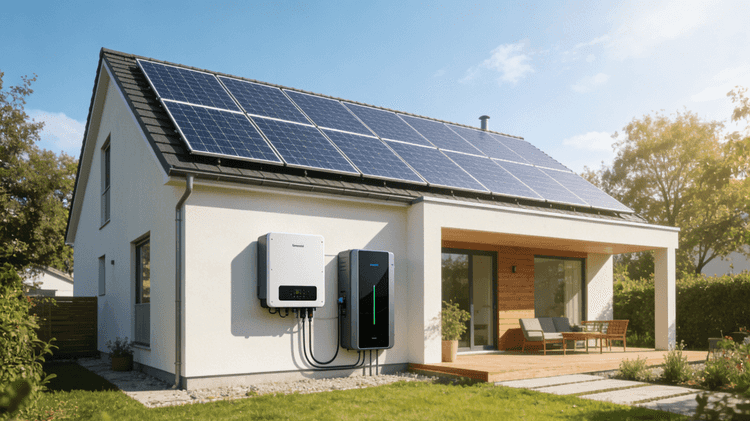
What is the Best Way to Store Electricity at Home? Exploring All-in-One Home Energy Storage Options
As the demand for renewable energy and energy independence grows, homeowners are increasingly seeking efficient and reliable ways to store electricity generated from renewable sources or during off-peak hours. All-in-One Home Energy Storage systems provide a means to store excess electricity for later use, reducing reliance on the grid and maximizing the benefits of renewable energy. In this article, we will explore different All-in-One Home Energy Storage options and evaluate the best ways to store electricity at home.
Understanding All-in-One Home Energy Storage
All-in-One Home Energy Storage involves capturing and storing electricity generated from renewable sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines, or storing electricity from the grid during periods of low demand. These stored energy reserves can be utilized during times of high demand or power outages, providing homeowners with greater control over their energy consumption and reducing dependence on the grid.
Different Household Battery Storage Options
1. Battery Residential Energy Storage Systems:
a. Lithium-Ion Batteries: Lithium-ion batteries are widely used in Residential Energy Storage Systems due to their high energy density, longer lifespan, and faster charging capabilities. These batteries are available in various sizes and capacities to accommodate different energy needs. They are particularly effective for residential applications, offering efficiency and versatility.
b. Lead-Acid Batteries: Lead-acid batteries have been used for Lithium Battery Home Storage for many years. While they are less efficient and have a shorter lifespan compared to lithium-ion batteries, they are typically more affordable. Lead-acid batteries are suitable for homeowners on a tighter budget or those with lower Lithium Battery Home Storage requirements.
2. Pumped Hydroelectric Storage:
Pumped hydroelectric storage is a large-scale Lithium Battery Home Storage option that involves using excess electricity to pump water from a lower reservoir to a higher reservoir. When electricity is needed, the water is released from the upper reservoir, flowing through turbines to generate electricity. While not directly applicable to individual homeowners, pumped hydroelectric storage plays a significant role in grid-level Lithium Battery Home Storage.
3. Thermal Storage:
Thermal Residential Energy Storage Systems in the form of heat or cold for later use. This can be achieved through the use of technologies like thermal batteries, phase change materials, or ice-based storage systems. Thermal storage is particularly suitable for applications such as space heating and cooling, where excess energy can be stored during off-peak hours and utilized when needed.
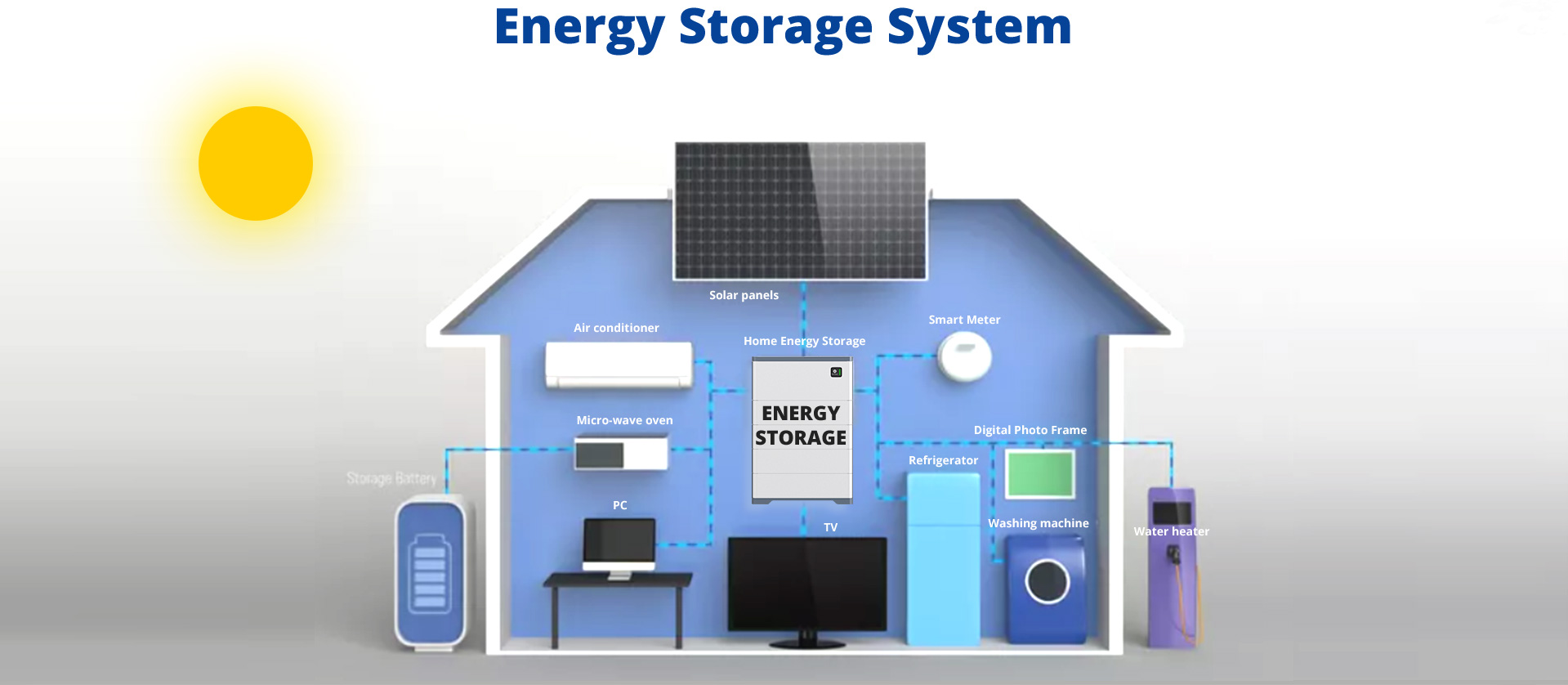
Factors to Consider for Lithium Battery Home Storage
1. Energy Needs: The first step in determining the best way to store electricity at home is to assess your energy needs. Consider factors such as the number of occupants, typical energy consumption patterns, and peak energy demands. This evaluation will help determine the appropriate storage capacity required for your home.
2. Cost: The cost of Residential Energy Storage Systems varies depending on the technology chosen, system size, and capacity. While lithium-ion batteries offer greater efficiency and longer lifespan, they come at a higher initial cost compared to lead-acid batteries. Consider your budget and evaluate the long-term cost-effectiveness of the chosen storage option.
3. Scalability: If you anticipate changes in your energy needs over time, it is important to choose a storage system that is scalable. This will allow you to increase or decrease the storage capacity as required without incurring significant additional costs.
4. Integration with Renewable Energy: If you have or plan to install a renewable Home Energy Storage System, such as solar panels, consider how the storage option integrates with the generation system. Ensure compatibility and assess the ability to capture and store excess energy efficiently.
5. Lifespan and Maintenance: Evaluate the expected lifespan of the storage system and the maintenance requirements associated with it. Lithium-ion batteries generally have a longer lifespan and require minimal maintenance compared to lead-acid batteries.
Choosing the best way to store electricity at home requires a careful evaluation of your energy needs, budget, and the available storage options. Residential Energy Storage Systems, including lithium-ion and lead-acid batteries, offer flexible and efficient solutions for residential Household Battery Storage. However, other options like pumped hydroelectric storage and thermal storage can also play a significant role in grid-level Household Battery Storage.
Consider factors such as cost, scalability, integration with renewable energy, lifespan, and maintenance requirements when selecting a Home Energy Storage System option. By making an informed decision based on your specific requirements, you can maximize the benefits of Household Battery Storage, reduce reliance on the grid, and move towards a more sustainable and self-sufficient energy future for your home.