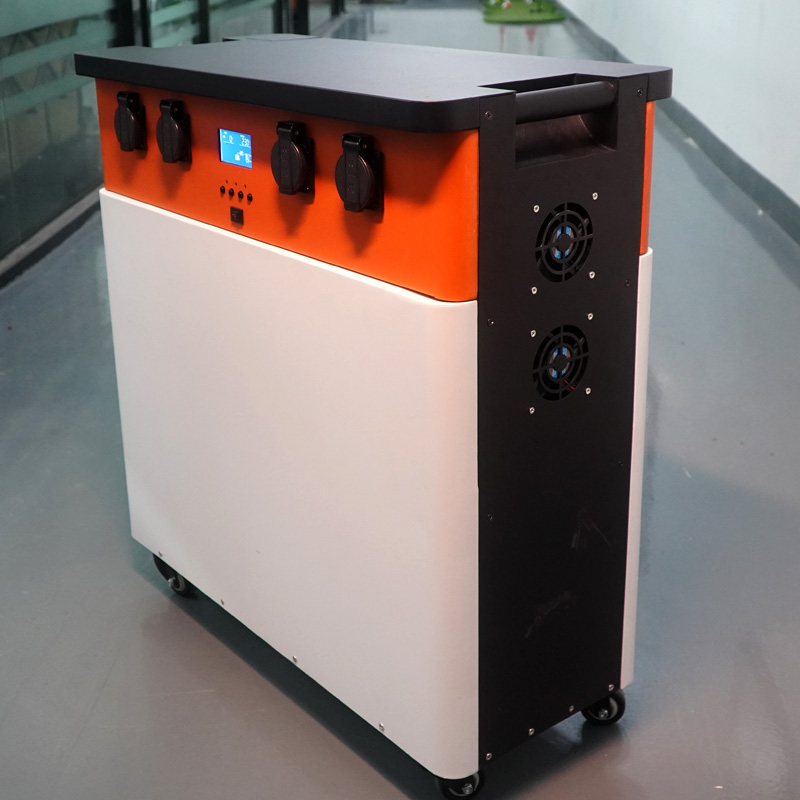
There are four considerations when choosing outdoor electricity for camping:
1. Power and battery capacity
When we camp outdoors, we need to use electrical appliances such as electric rice cooker, induction cooker, barbecue grill, electric hot pot, small fan, etc. To support the use of these electrical appliances, we need a portable battery station with a power of about 1000W and a battery capacity of 600- 800Wh.
2. Security
The batteries used in portable battery stations on the market are mainly ternary lithium batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries. The cycle life of the former is about 500 times, and the cycle life of the latter is at least 4,000 times. For ternary lithium batteries and lithium iron phosphate batteries of the same volume, the former has larger capacity and better stability. If your requirements for capacity are not so high, it is best to choose the portable battery station of lithium iron phosphate batteries. partastar portable battery station adopts lithium iron phosphate battery, so that it basically prevents energy problems before your battery explodes and catches fire.
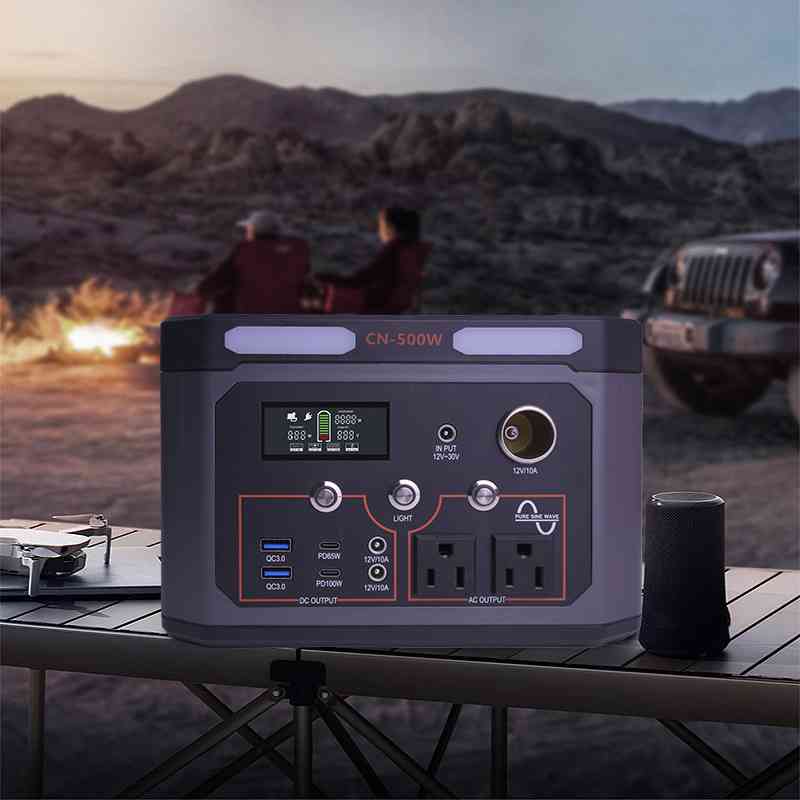

2. Whether it supports multiple charging and power supply methods
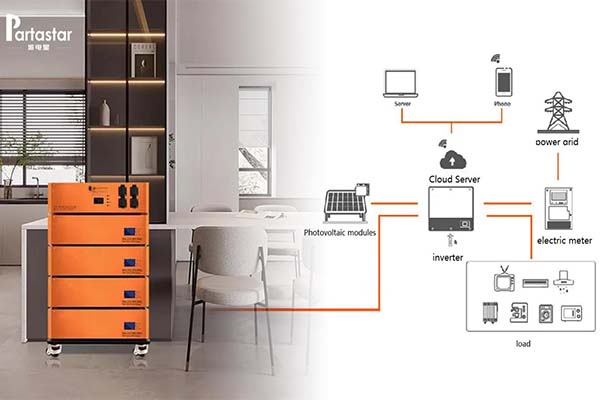
Solar charging, I think this is a very important point!
Because when camping outdoors, no charging method is as good as solar charging. When the portable battery station is low in power, it can be directly connected to the solar panel to provide power while charging the portable battery station, which is convenient and environmentally friendly.
Of course, car charging is also an essential charging method for outdoor camping!
When traveling outdoors, if the portable battery station suddenly runs out of power, it is not so easy to find a place to charge it. It would be much more convenient if the portable battery station could support on-board charging.
partastar portable battery station can supply power to 10 devices at the same time, and has 5 types of interfaces: AC, DA, Type-C, USB-A, and car charger, so that you no longer have to worry about insufficient power consumption.