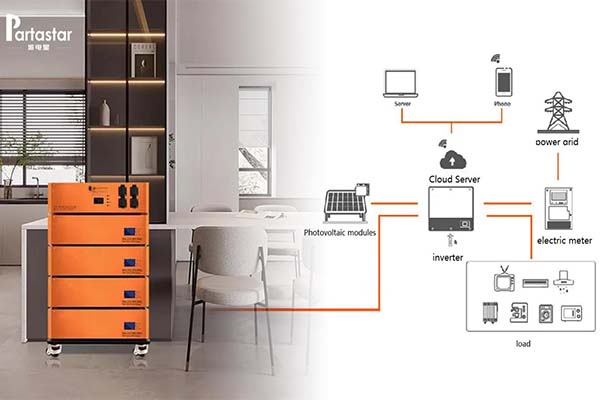
With the increasing emphasis on renewable energy and the desire for energy independence, many homeowners are exploring ways to store excess energy generated from renewable sources for later use. Home energy storage systems provide a solution by allowing homeowners to store and utilize energy efficiently. In this article, we will explore different methods and technologies for storing energy at home, their benefits, and considerations for implementing such systems.
1. Battery Storage Systems:
Battery storage systems are a popular choice for home energy storage. These systems utilize rechargeable batteries to store excess energy generated from renewable sources, such as solar panels or wind turbines. Lithium-ion batteries are commonly used due to their high energy density, long cycle life, and efficiency. Battery storage systems allow homeowners to store energy during periods of low demand or high renewable energy generation and use it during peak demand or when renewable energy generation is low.
2. Benefits of Battery Storage Systems:
Battery storage systems offer several benefits for homeowners. Firstly, they provide backup power during grid outages, ensuring a continuous power supply for essential devices and appliances. Secondly, battery storage systems allow homeowners to maximize their utilization of renewable energy, reducing reliance on the grid and potentially lowering electricity bills. Additionally, battery storage systems contribute to a more sustainable and resilient energy infrastructure by enabling the integration of renewable energy sources.
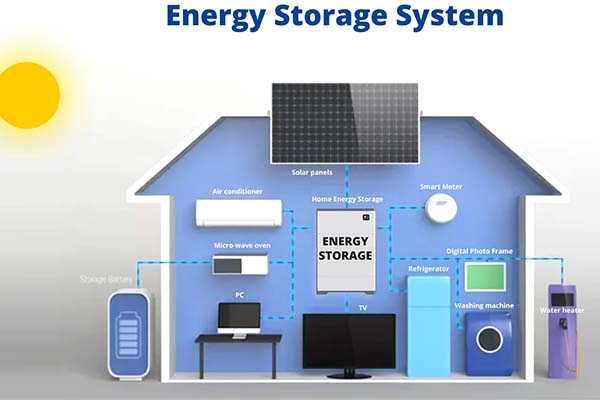
3. Considerations for Battery Storage Systems:
When considering a battery storage system for home energy storage, several factors should be taken into account. The capacity of the battery system should be carefully assessed to meet the household's energy needs during periods of low renewable energy generation or grid outages. The system's efficiency, including charge and discharge rates, should also be considered to optimize energy utilization. Additionally, it is essential to evaluate the upfront costs, maintenance requirements, and warranties associated with the battery storage system.
4. Pumped Hydro Storage:
Pumped hydro storage is a well-established method for large-scale energy storage, but it can also be adapted for home energy storage on a smaller scale. This system uses excess energy to pump water from a lower reservoir to a higher reservoir, storing potential energy. When energy is needed, the water is released back to the lower reservoir, passing through turbines to generate electricity. Pumped hydro storage offers high efficiency and long cycle life, but it requires suitable topography and access to water sources.
5. Thermal Energy Storage:
Thermal energy storage systems store energy in the form of heat for later use. One common method is through the use of phase change materials (PCMs). These materials absorb and release thermal energy during phase transitions, such as melting and solidification. Heat generated from renewable sources, such as solar thermal panels or biomass boilers, can be stored in PCMs and used for space heating, hot water, or other thermal applications when needed. Thermal energy storage systems offer high efficiency and can be integrated into existing heating systems.
6. Flywheel Energy Storage:
Flywheel energy storage systems store energy in the form of rotational kinetic energy. Excess energy is used to accelerate a flywheel to high speeds. When energy is needed, the flywheel's rotational energy is converted back to electricity. Flywheel energy storage systems offer fast response times, high power density, and long cycle life. However, they may have limited energy storage capacity and require a controlled environment to minimize energy losses due to friction.
7. Hydrogen Energy Storage:
Hydrogen energy storage involves the production and storage of hydrogen gas using excess renewable energy. Electrolysis is used to split water into hydrogen and oxygen, with the hydrogen stored in tanks or underground storage facilities. When energy is needed, the stored hydrogen can be converted back to electricity through fuel cells or combustion engines. Hydrogen energy storage offers high energy storage capacity and can be used for both electricity and heat generation. However, it requires additional infrastructure and has efficiency losses during conversion processes.
Home energy storage systems provide homeowners with the ability to store excess energy generated from renewable sources and utilize it efficiently. Battery storage systems are commonly used and offer benefits such as backup power, increased utilization of renewable energy, and grid independence. Pumped hydro storage, thermal energy storage, flywheel energy storage, and hydrogen energy storage are alternative methods that can be suitable depending on s