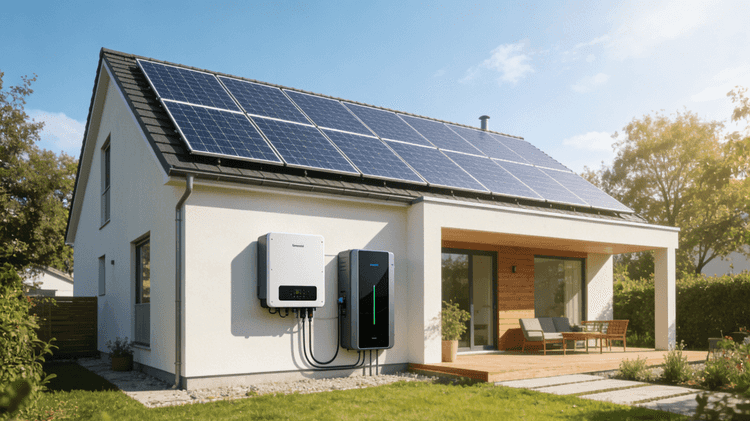
When it comes to portable power Smart Storage Solutions, two popular options that often come to mind are lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations and generators. While both serve the purpose of providing electrical power, there are significant differences between the two technologies. In this article, we will explore the dissimilarities between lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations and generators, shedding light on their functioning, advantages, limitations, and use cases. Understanding these distinctions will help individuals and businesses make informed decisions when selecting the most suitable power Smart Storage Solutions for their specific needs.
1. Technology and Power Generation:
1.1. Lithium Stackable Home Battery Power Stations:
Lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations, as the name suggests, utilize advanced lithium-ion Stackable Home Battery technology to store electrical energy. These power stations are essentially large-scale, portable batteries that can be recharged using various sources such as solar panels, wall outlets, or car chargers. The stored energy can then be used to power electronic devices or appliances through built-in AC outlets, DC ports, or USB ports.
1.2. Generators:
Generators, on the other hand, employ combustion engines or alternative fuel sources to generate electricity. Common types include diesel, gasoline, propane, or natural gas generators. These engines are connected to an alternator, which converts mechanical energy into electrical energy. Generators produce AC power that can be used to run appliances and devices directly or through an electrical distribution system.
2. Portability and Convenience:
2.1. Lithium Stackable Home Battery Power Stations:
Lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations are designed with portability in mind. They are compact, lightweight, and easy to transport, making them ideal for outdoor activities, camping trips, or emergency power backup. These power stations eliminate the need for fuel and do not produce noise or emissions during operation, providing a quiet and eco-friendly power solution.
2.2. Generators:
Generators, particularly those powered by combustion engines, tend to be bulkier, heavier, and less portable compared to lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations. They require a constant supply of fuel and often emit noise and exhaust fumes during operation. While some portable generator models are available, they still require fuel storage and regular refueling, which can be inconvenient in certain situations.
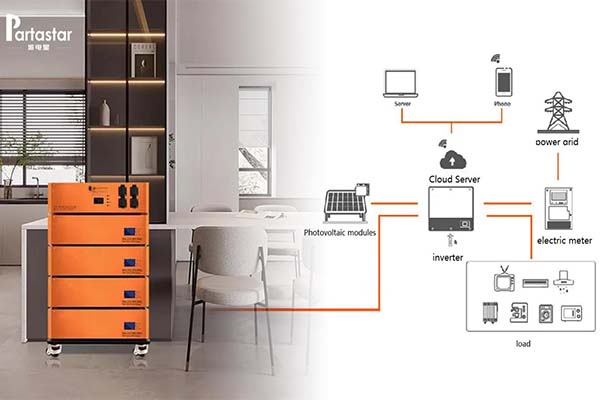
3. Power Output and Capacity:
3.1. Lithium Stackable Home Battery Power Stations:
Lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations typically offer a range of power output options, from small portable units capable of charging smartphones and laptops to larger models that can power appliances, tools, or even small-scale electrical systems. The power output of these stations is measured in watts (W) and can vary depending on the model and capacity. They provide a stable power supply with no fluctuations, making them suitable for sensitive electronic devices.
3.2. Generators:
Generators are available in various sizes and power ratings, ranging from small portable units to large industrial-grade models. They offer higher power output capacities compared to lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations, making them suitable for running heavy-duty appliances, construction equipment, or backup power for buildings. Generators can handle power surges and startup loads better than most lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations.
4. Runtime and Recharging:
4.1. Lithium Stackable Home Battery Power Stations:
Lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations provide a specific runtime based on their energy capacity, measured in watt-hours (Wh) or ampere-hours (Ah). The runtime can vary depending on the power demand of connected devices or appliances. These power stations can be recharged using various sources, such as solar panels, AC outlets, or vehicle chargers. The recharging time can range from a few hours to several hours, depending on the charging method and the capacity of the power station.
4.2. Generators:
Generators offer extended runtime as long as there is a continuous supply of fuel. The runtime depends on the fuel capacity and the efficiency of the generator. With larger fuel tanks, generators can operate for longer durations without the need for refueling. However, refueling interrupts the power supply and requires additional fuel storage and handling.
5. Environmental Impact:
5.1. Lithium Stackable Home Battery Power Stations:
Lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations have a minimal environmental impact as they do not produce emissions during operation. They rely on clean energy sources such as solar power or grid electricity for recharging, further reducing carbon footprint and dependence on fossil fuels.
5.2. Generators:
Generators powered by combustion engines produce noise, exhaust emissions, and carbon emissions during operation. While advancements in generator technology have led to reduced emissions and improved fuel efficiency, they still contribute to air and noise pollution to some extent.
Conclusion:
Lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations and generators offer distinct power solutions with varying characteristics, advantages, and limitations. Lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations excel in terms of portability, convenience, quiet operation, and environmental friendliness. They are suitable for applications that require clean, silent power without the need for constant refueling. Generators, on the other hand, provide higher power output capacities, longer runtimes, and the ability to handle heavier loadsand power surges. They are typically used in situations where a continuous power supply is needed for extended periods, such as construction sites, outdoor events, or as backup power for homes or businesses.
When choosing between a lithium Stackable Home Battery power station and a generator, it's important to consider factors such as portability, power output requirements, runtime needs, and environmental impact. Lithium Stackable Home Battery power stations are well-suited for individuals or businesses seeking a portable, clean energy solution with moderate power requirements. Generators, on the other hand, are better suited for applications that demand higher power output capacities and longer runtimes, albeit at the cost of increased noise and emissions.
By carefully evaluating your specific needs and considering the advantages and limitations of each technology, you can make an informed decision on whether a lithium Stackable Home Battery power station or a generator is the right choice for your power requirements. Ultimately, both options provide valuable Smart Storage Solutions, and the choice depends on the unique demands of your situation.